A Beginners Guide to Music Theory
Music theory might sound like a complex term, but it’s simply the roadmap to understanding how music works. It’s like uncovering the secrets behind your favourite songs—the patterns, notes, and structures that make them sound the way they do. In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of music theory in a clear, step-by-step manner, perfect for beginners diving into the world of music.
What is Music Theory?
You don’t need to be a musical genius to grasp the concepts of music theory. It’s all about discovering the fundamental building blocks of music—notes, scales, chords, rhythm, and more. These elements form the backbone of every melody, harmony, and rhythm you hear in a song. Let’s start by exploring the bedrock of Music Theory – notes and scales.
Notes and Scales
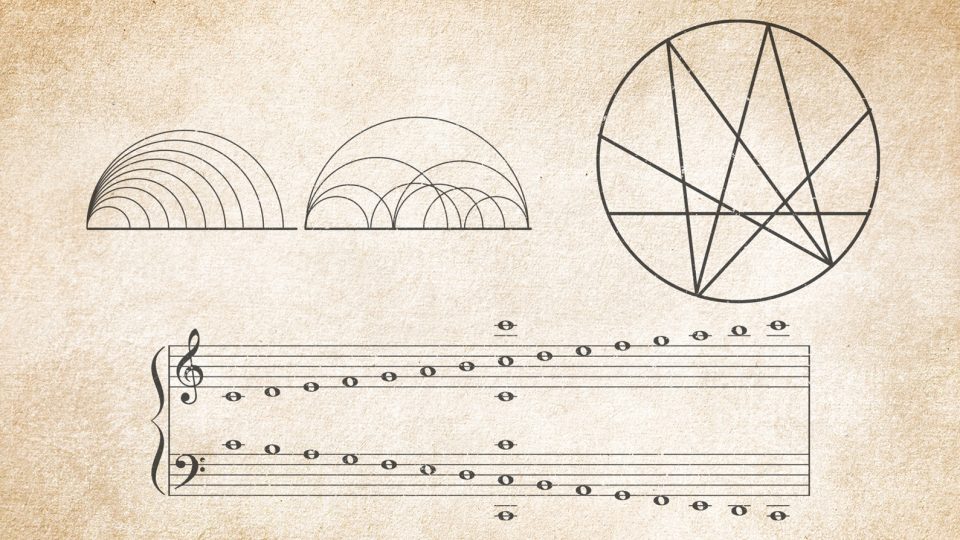
Music finds its essence in notes. They’re like the musical equivalent of the alphabet, forming melodies when arranged in specific sequences. And like the alphabet they are assigned a letter from A through to G. Every note possesses a distinct pitch, which defines its highness or lowness in the auditory spectrum. The higher keys produce higher-pitched notes, while the lower keys resonate with lower-pitched notes. This pitch variation allows musicians to create melodies that soar or descend. This grouped sequence of ascending keys is further assembled into octaves. (see the image below)

Musical Scales
Scales, on the other hand, are sequences of notes arranged in ascending or descending order. They lay the groundwork for creating melodies and harmonies. The most common scale, the major scale, consists of eight notes in a specific pattern of whole and half steps. There are however hundreds of different musical scales. Different countries and cultures often have their own unique scales. These ‘world’ scales vastly influence the sound of the music being played.
In the realm of music theory, notes and scales set the stage for further exploration into intervals, chords, rhythm, time signatures, key signatures, and modes.
Elements of Music Theory
Intervals and Chords
Intervals are the distances between two notes. They define the relationship between pitches, whether they sound harmonious or create tension. For instance, a perfect fifth interval is the foundation of power chords in rock music, while a minor second creates a dissonant, eerie sound.
Chords are formed by combining multiple notes played simultaneously. The most basic chord, the triad, consists of three notes—root, third, and fifth—stacked on top of each other. Understanding chords is like unlocking the door to harmonization in music.
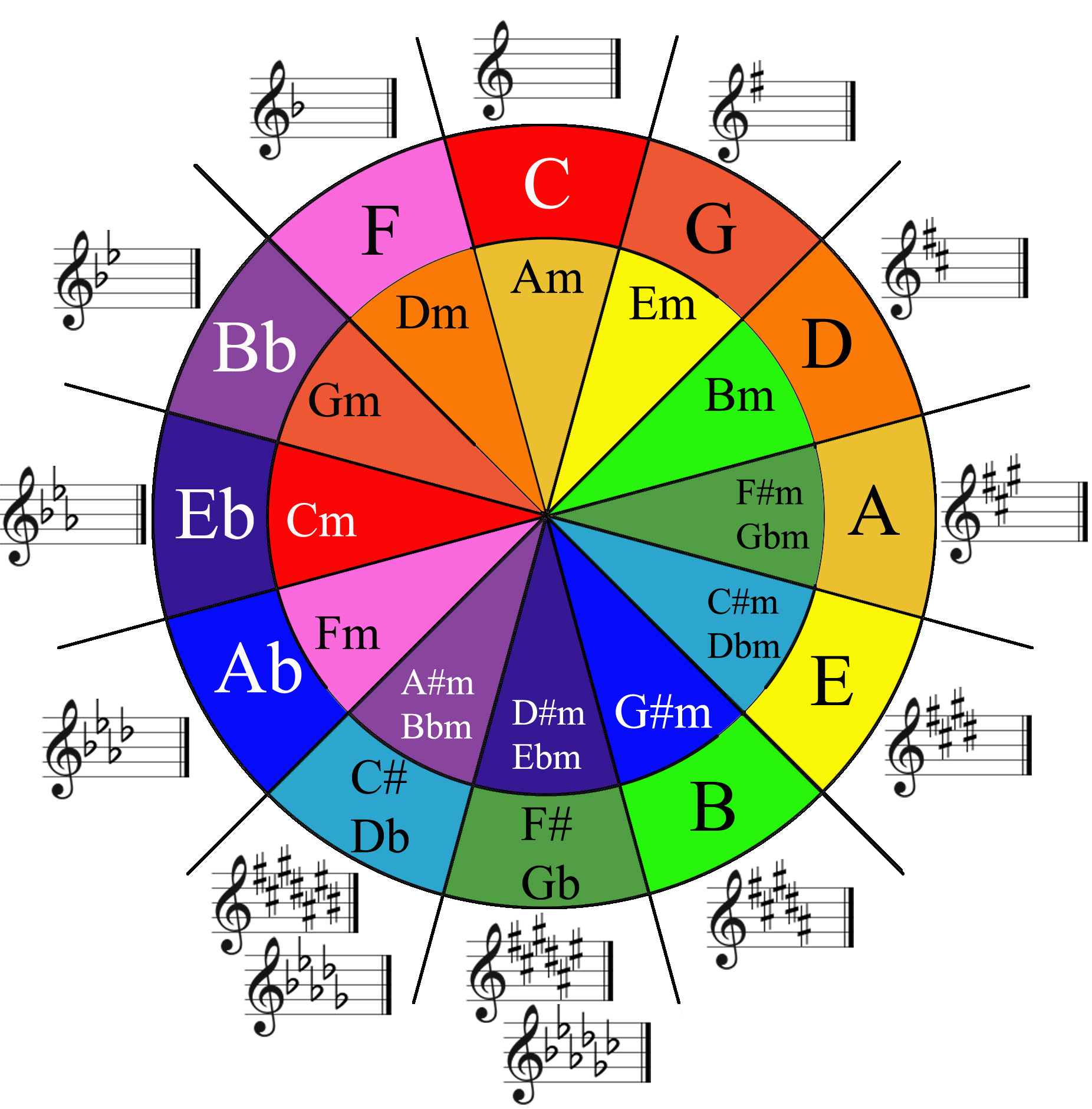
Once you have grasped the basics of Chord formation you may want to check out a useful tool called the circle of fifths. It’s a visual representation showing the relationship between different keys in music. The circle displays all 12 major and minor keys arranged in a circular shape.
Moving clockwise around the circle, each key is a fifth apart from the previous one. For instance, starting from C major, you move to G major, then D major, and so on. This relationship helps musicians understand the connections between keys and how they relate harmonically.
The circle of fifths can be a valuable reference when trying to understand keys and scales. Compositionally it can help you determine key selection, chord progressions, and understand the relationships among different musical keys. For a more detailed explanation of the circle of Fifths check out this post. https://create.routenote.com/blog/key-signatures-and-the-circle-of-fifths/
Rhythm and Time Signatures
Rhythm is the heartbeat of music. It’s the pattern of long and short sounds that create a groove or pulse. Time signatures, represented by numbers like 4/4 or 3/4, dictate the rhythm by indicating the number of beats per measure and the type of note that receives one beat. For example, 4/4 time means four beats per measure, with the quarter note getting one beat.
Mastering rhythm and time signatures lays the groundwork for musicians to play in sync, ensuring a cohesive musical performance. It’s also a crucial aspect to grasp when producing within a DAW as it determines the rhythmic structure of a session.
Key Signatures and Modes
Key signatures define the tonality of music, indicating which notes are sharp or flat throughout a piece. They provide the framework for melodies and harmonies, establishing the musical “home.”
Modes are variations of scales, each with its unique sound and mood. Understanding modes allows musicians to explore different tonalities, adding depth and richness to compositions.
Practical Application of Music Theory
Song Structure
Understanding music theory gives insight into the architecture of songwriting. Songs often follow a familiar structure comprising verses, choruses, bridges, and more. These sections, guided by music theory principles, create a narrative within the music. For instance, a chorus typically repeats melodically and lyrically, providing a central theme, while verses advance the story or message.
Analysis of Famous Songs
Analyzing popular songs through the lens of music theory can be enlightening. Take a favourite song and dissect it—identify the chords, analyze the progression, and observe the use of rhythm and time signatures. This exercise unveils how theory is applied in real compositions, deepening your understanding of musical structure.
Tips for Learning Music Theory
Practice Techniques
Consistency is key when learning music theory. Dedicate regular time to practice. Start with simple exercises like identifying notes on a piano or recognizing intervals. Gradually progress to more complex tasks, such as building chords and chord progressions or sight-reading melodies.
Resources and Tools
Fortunately, numerous resources can aid your music theory learning. Books like “Music Theory for Dummies” by Michael Pilhofer and Holly Day or online platforms like musictheory.net offer structured lessons and exercises. Additionally, apps such as Tenuto and Perfect Ear provide interactive tools for practice.

Common Challenges
Learning music theory might present challenges, especially in grasping abstract concepts like modes or complex rhythms. Patience is key as you navigate through these concepts. It’s normal to find certain aspects challenging. Stick with it and eventually, these concepts will become embedded.
Strategies for Success
Break down complex topics into smaller, manageable parts. Seek clarification from teachers, peers or online forums if needed. Additionally, practical application by playing or composing music can solidify theoretical concepts. Remember theory isn’t everything and musical feel is equally important. Don’t loose sight of this as it’s ‘feel ‘that will inject originality and your unique character into your music compositions.
Conclusion
Remember that music theory isn’t a set of strict rules but rather a guide that empowers musicians to create, understand, and appreciate music more deeply. By grasping these foundational elements, you’re equipped to explore the endless possibilities within music.
Continue by applying these theories practically, whether through playing an instrument, composing, or simply listening actively to different genres. Embrace the learning process, and over time, these concepts will become second nature, enriching your musical experience.
Music theory may seem daunting at first, but with consistent practice, patience, and an eagerness to learn, you’ll unlock the door to a whole new dimension of musical understanding.
Until next time, keep exploring, keep practising, and keep that creativity flowing.
Remember – RouteNote Create subscriptions start from as little as $2.99. You also get 10 FREE credits to spend on samples along with access to our FREE sample pack bundle when you sign-up!