What is mid-side EQ and how can it help your mixes?
So you may have heard the term mid-side EQ banded about in regards to mixing. But what does it actually refer to? In this guide, we will be taking a trip to the mid-side, and help to shed some sonic light on this most useful function.
Knowing your mid-side
Mid-side EQ is a sophisticated technique that helps give you more control over the mixing process. It offers engineers and producers a powerful tool to shape and manipulate stereo sound. Unlike traditional EQ which acts upon the full stereo field, mid-side EQ allows for independent control over the center (mid) and side (stereo) components of a stereo signal.
In essence, mid-side EQ separates the mono content from the stereo content allowing you to process either one separately. This can be particularly useful as traditionally certain elements of a track sit in distinct areas of a stereo field. For example vocals, bass, and kick drums tend to be centred in a mix (mono) while wide-panned instruments, spatial effects and ambient sounds tend to dwell on the sides of a stereo mix. Mid-side EQ can therefore home in on specific areas of a stereo mix allowing for precise adjustments to be made.
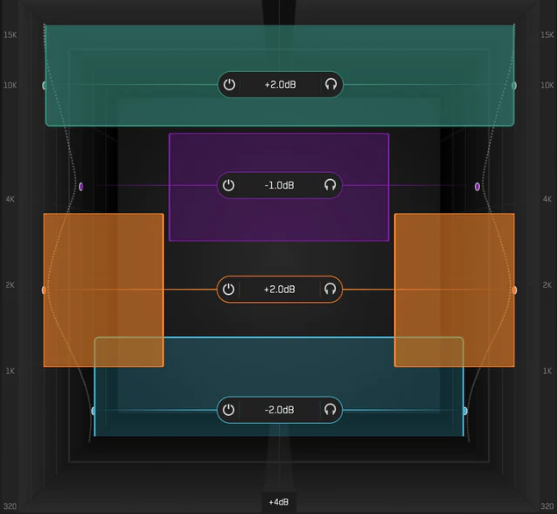
Mid-side EQing in mastering scenarios
Mid-side EQ is largely used in the field of mastering. It allows for a level of detailed control that isn’t possible using standard EQ. It can help with corrective work as well as to enhance or tame a track’s overall energy. As long as a stereo mix conforms to standard panning practices this technique allows you to target and effect certain elements without disturbing other aspects of the mix. Here are a few examples of where mid-side EQ could help you in a mastering session.
Controlling Bass and Kick Balance: Mid-side EQ is effective in balancing the low-end energy of a track, especially between the bass and kick drum. By boosting or cutting specific frequencies in the mid signal, you can enhance the punch and clarity of the kick without affecting any other low-end elements in a mix that might reside on the side signals. Simultaneously, adjustments in the side signal can help manage the stereo spread of low frequencies without compromising mono compatibility. As the sub-frequencies should generally reside in the mono realm, eliminating any stereo-field sub-frequencies can help to increase overall headroom. It can also assist in giving your bottom end more definition and help tame any muddiness in a mix.
Addressing Frequency Build-Ups: In complex arrangements with multiple instruments, mid-side EQ can help address frequency build-ups and resonances that can muddy the mix. By identifying problematic frequencies in the mid or side signal using frequency analyzers or spectral meters, you can apply surgical EQ cuts to mitigate masking and improve overall clarity and separation.
Balancing Vocals and Instruments: In a mix where vocals compete with wide-panned instruments like synths or guitars, mid-side EQ can be applied to create more space and clarity. You can boost the mid frequencies of the vocals to make them more prominent and cut the corresponding frequencies in the side signal to reduce masking and avoid clashes with other elements.
Using mid-side in the mix
Because mid-side EQ is effective over a full stereo track there are not as many applications within traditional mixing methods. This is because you have all the elements on individual tracks giving you the power to manipulate the EQ and panning of each track. There are however a few situations when this technique can be useful.
Sample re-balancing: The first is when you are working with samples that are full musical compositions. You may want to try to rebalance the levels within a stereo sample. For instance, you might want to try and bring a vocal out a little more. Or you may want to play your own bassline over a sample. In this case you could identify and cut the sample’s bass frequencies without affecting the rest of the low end that resides on the sides. Alternatively, you may want to try and add a little top-end sheen to a sample without affecting the vocal or drums that tend to reside in the centre. Boosting hi-mids and top end to the sides only will help retain the integrity of the sample’s main core while helping to produce an airy quality. It can also help to give the impression of a widened stereo field.
Ensemble recordings: If part of your mix involves a stereo ensemble recording then mid-side EQ can help this to sit. It could be a recording of a choir in a large space where you want to tame some of the stereo room ambience. Live orchestration can also be controlled in much the same way.
Drum Overhead and Room Mic recordings: If your drum track involves a stereo overhead or room recording then mid-side EQ can help to clean up any unwanted frequencies. For example, you may have a loud splashy cymbal and the high frequencies are getting in the way of the mix and cutting through too much. If this cymbal resides mainly in the stereo field, you could perform a tight curve cut on the troublesome frequency in the side field.
Mid-side EQ List
So you like the sound of all this mid-side EQing and want to see what it can do for your mixing? Finally, let’s take a look at some popular EQs that feature mid-side processing.
4: Waves H-EQ Hybrid Equalizer.
7: DMG EQuick
Remember – RouteNote Create subscriptions start from as little as $2.99. You also get 10 FREE credits to spend on samples along with access to our FREE sample pack bundle when you sign-up!